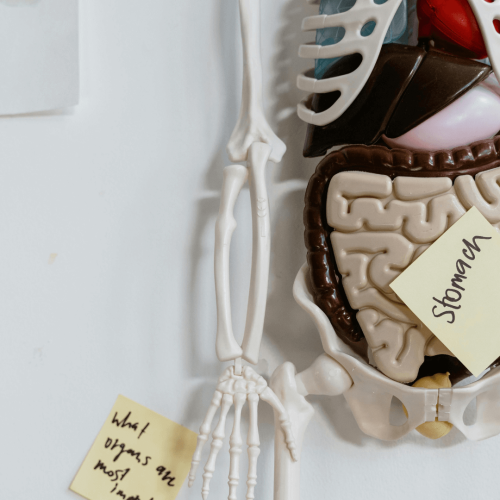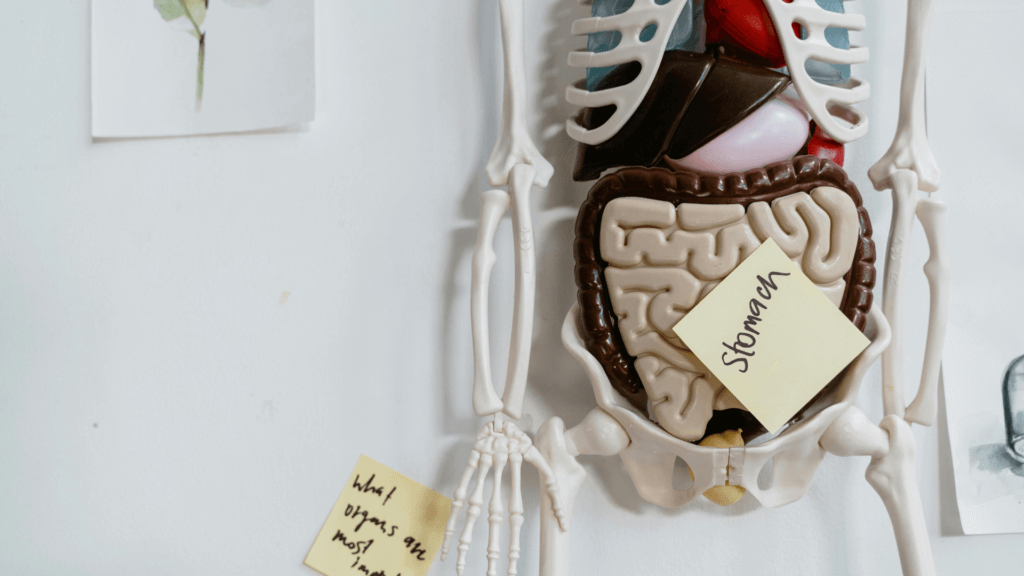
In today’s world, food allergies have become increasingly common. From celiac disease and wheat allergies to lactose intolerance and soy sensitivity, many people struggle with digestive issues. The root cause of these problems often lies in the gut. Bad bacteria overgrowth weakens immunity, disrupts digestion, and can cause a range of health issues, including slow metabolism, irregular appetite, and nutritional deficiencies.
The Role of Gut Health in Nutrient Absorption
No matter how much nutrition you consume, if your gut is unhealthy, your body won’t be able to absorb and utilize essential vitamins and minerals. Deficiencies in Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D, for instance, are closely linked to poor gut health. If your digestive system is not functioning properly, symptoms like muscle cramps, bone weakness, and even fever-like sensations may arise.
Additionally, the vagus nerve, which connects the stomach to the brain, plays a crucial role in sending signals related to digestion and emotions. When gut health is compromised, it can lead to mood swings, stress, and even depression. Hormonal imbalances, difficulty swallowing, and increased cholesterol levels are all linked to poor digestion.
The Impact of Overeating on Digestion
Overeating is a significant contributor to digestive issues. The human stomach is only the size of a fist, yet we often overfill it, leading to bloating, indigestion, and an inability to properly digest food. When you eat too much at once, digestive enzymes struggle to break down food efficiently, which slows down metabolism. The key is to eat until you’re about 75% full, chew slowly, and avoid distractions while eating, such as watching TV.
Studies suggest that it takes at least 18 minutes for the brain to receive signals from the stomach that it is full. Eating too quickly prevents this mechanism from working properly, which can lead to overeating and weight gain.
Coffee, Alcohol, and Their Effect on Gut Bacteria
Coffee, when mixed with milk, has an impact on gut bacteria. Similarly, alcohol and nicotine affect gut flora, disrupting the balance of good and bad bacteria. The body produces beneficial bacteria overnight, but consuming tea or coffee first thing in the morning can kill these beneficial microbes. This is why probiotics and prebiotics are crucial for maintaining gut health.
- Prebiotics are the fiber-rich foods that feed good bacteria.
- Probiotics are live bacteria that help maintain a healthy digestive system.
Without probiotics, gut health declines, leading to issues such as bloating, constipation, and inflammation.
The Role of Bacillus Coagulans in Gut Health
One of the most beneficial probiotics is Bacillus Coagulans, which plays a crucial role in digestion, particularly in breaking down proteins and carbohydrates. Studies show that this probiotic can help with rheumatoid arthritis, constipation, bloating, and gas. Additionally, it supports respiratory health by enhancing immune system function.
Diet and Gut Microbiome
A vegetarian and vegan diet has a significant impact on gut microbiome health. Unlike an animal-based diet, which lacks fiber, a plant-based diet provides the necessary fiber for healthy gut bacteria. Fiber is essential for producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate, propionate, and butyrate, which help prevent leaky gut syndrome.
Consuming a variety of plant-based foods enhances gut health. A diet rich in colorful fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports a diverse microbiome. Avoiding fried, spicy, and overly sweet foods is also key to reducing inflammation and maintaining a balanced gut.

The Connection Between Stress and Gut Health
The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” because of its direct connection to mental health. Stress can lead to the overgrowth of bad bacteria while decreasing good bacteria. Studies show that both physical and emotional stress negatively impact gut flora.
In one study, a cat that was frightened by a dog stopped producing digestive juices for eight hours due to stress. Similarly, in humans, stress weakens the immune system and slows digestion, leading to problems like indigestion, bloating, and constipation.
The Importance of Dietary Variety
Most of the world’s food comes from just 12 types of grains and 5 types of animals. However, consuming the same food every day can harm gut health. Different bacteria require different nutrients, so eating a diverse diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains helps maintain gut balance.
Colors in food represent different antioxidant properties. For example:
- Green foods (spinach, kale, green chilies) support detoxification.
- Yellow and orange foods (carrots, turmeric, mangoes) are rich in vitamins.
- Red foods (tomatoes, berries) provide powerful antioxidants.
Eating a variety of colors ensures that you receive a wide range of nutrients that support gut health and overall wellness.
Inflammation, Weight Gain, and Gut Health
Inflammation is the body’s response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it leads to serious health issues. High levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) indicate inflammation, which is closely linked to obesity. Even a 5-kilogram weight gain can increase inflammation and damage the intestines.
Excess abdominal fat compresses the intestines, leading to constipation, indigestion, and increased stress on the digestive tract. This is why maintaining a healthy weight is essential for good gut health.
The Risks of Overstraining During Bowel Movements
Many people spend too much time in the toilet, straining excessively to pass stool. This can lead to conditions such as hernia and prostate issues. Instead of forcing bowel movements, maintaining a fiber-rich diet and drinking enough water will naturally regulate digestion and prevent constipation.
The Dangers of Excessive Wheat Consumption
Modern wheat is genetically modified and contains high levels of gluten, which many people find difficult to digest. Gluten sensitivity can lead to issues such as bloating, fatigue, and leaky gut syndrome. Instead of relying solely on wheat, incorporating millets into the diet can provide better nutrition and be gentler on the digestive system.
The Risks of Overstraining During Bowel Movements
Essential Nutrients for Gut Health
To support gut health, include the following in your diet:
- Probiotics (yogurt, fermented foods, supplements)
- Prebiotics (fiber-rich foods, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables)
- Hydrating foods (coconut water, fruit juices, soaked basil seeds)
- Collagen-boosting foods (bone broth, ghee, aloe vera juice)
Final Thoughts
Your gut health influences your immunity, mental well-being, and overall vitality. By making mindful dietary choices, managing stress, and incorporating probiotics and fiber into your diet, you can maintain a healthy digestive system and prevent numerous health issues. Take care of your gut, and it will take care of you!